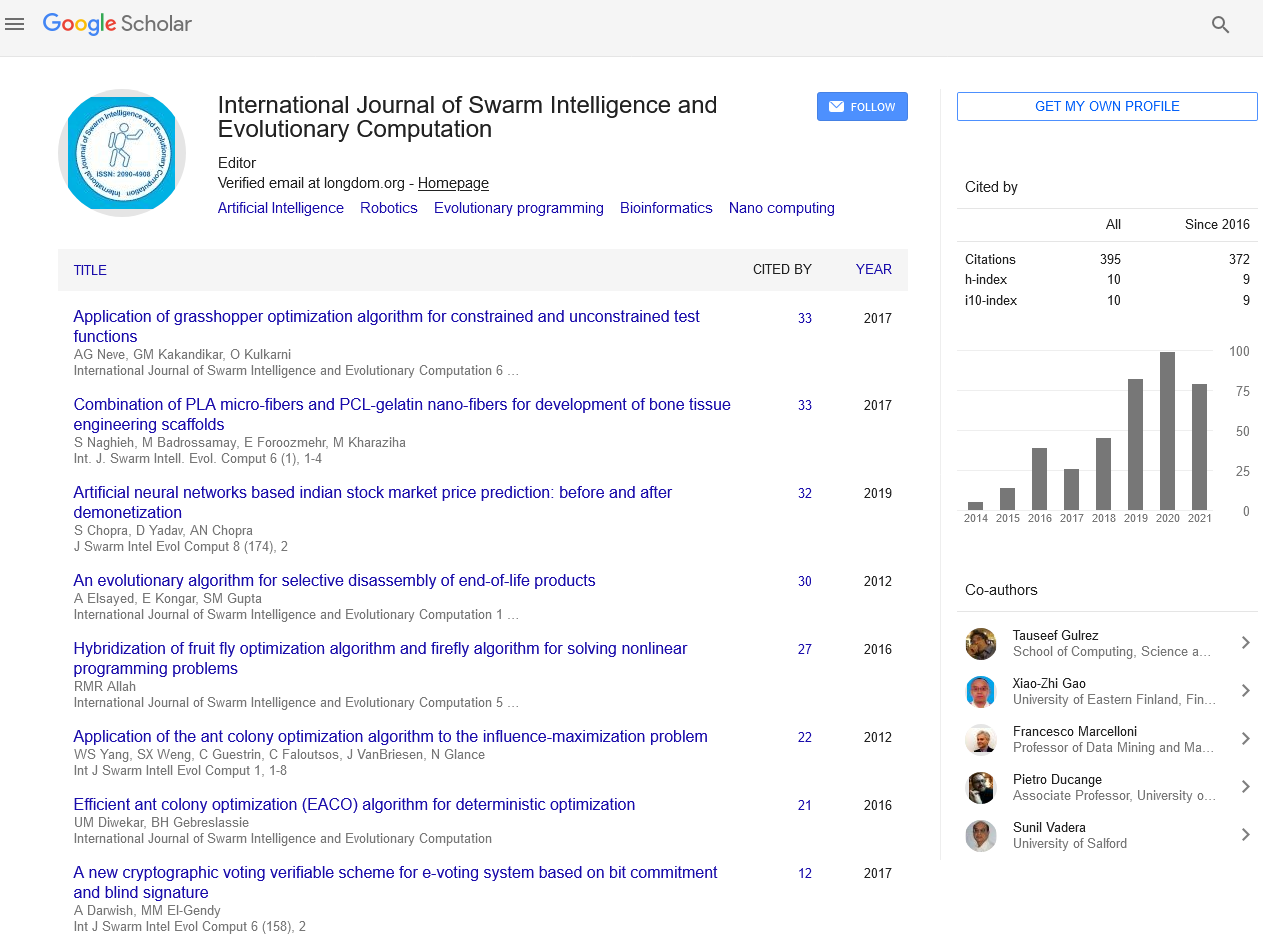
Indexed In
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Commentary - (2021) Volume 0, Issue 0
What is Artificial Immune System?
Xin-Wu Deng*Received: 06-Oct-2021 Published: 27-Oct-2021, DOI: 10.35248/2090-4908.21.s6.002
Description
Artificial Immune Systems (AISs) are sophisticated algorithms that are based on principles that are inspired by the human immune system. AISs are a key methodology that uses a computationally intelligent and rules-based machine learning strategy inspired by the ideas and procedures of the vertebrate immune system. It is concerned with the immune system's involvement in computational structures, as well as its extension and study of the use of such methods to solve analytical issues in engineering, mathematics, and information science.
This methodology is a subfield of biologically inspired computation and natural computation, with advances in machine learning and contributions to Artificial Intelligence (AI) in particular. Artificial immune systems are a sort of adaptive system that is built on resistant goals and abstract immunology, with laws and prototypes being utilized to address problems. It's a computational paradigm that emerged through connections and alliances between immunologists and computer scientists in the development of algorithms prompted by the immune system of vertebrates. It brings together and promotes the fields of immunology, computer science, and engineering. The immune system's properties of detection, diversity, tolerance, and learning have been highlighted, and channel Artificial immune systems with the ability to adapt to changing situations and effective for problem-solving tasks such as pattern recognition, learning and memory acquisition, distributed detection, and optimization, among others, have been developed. The AIS algorithms created are adaptive in nature, as evidenced by adaptive immunological cells such as B-cells, Tcells, and dendritic cells, according to the definition supplied. An artificial immune system employs some of the engineering techniques used in biological immune systems to create algorithms or technologies that address systemic goals. This could include immune system mathematics and computer modeling, as well as the abstraction of some immunology principles into algorithms. In the 1980s, the concept of artificial immune systems began to take shape. The complicated human immune system has been discovered to be an excellent model for generating machine learning and artificial intelligence findings that apply a form of "game theory" to how humans' immune systems work, according to researchers. Readers can find more information about specific projects, as well as available jobs and internships, on AISWeb, the online home of artificial immune systems, as well as links to international research on the idea of using the immune system to put together new types of artificial intelligence projects. Artificial Immune Systems (AISs) are computational approaches inspired by the biological immune system, and are thus categorized as a type of nature-inspired meta-heuristic along with genetic algorithms, ant colony optimization, particle swarm optimization, and others. Optimization is a mathematical principle that is widely used in many sorts of engineering to solve design and operational difficulties, as well as a tool for defining and addressing inverse problems like parameter identification in scientific and engineering contexts. The key contributions are compared and contrasted with the various principles of the biological immune system that have inspired such strategies, such as clonal selection, hypermutation, immunological network, affinity, and so on. The four main types of optimization problems are considered: Unconstrained problems, constrained problems, multimodal problems, where several optima are to be obtained in a single run, and multi-objective problems, where an approximation to the Pareto set is to be obtained as the result of a single run of the algorithm. Although AISs are effective at solving optimization problems, they can be improved by combining features from other techniques with "pure" AIS to create hybrid AIS methods.
Citation: Deng XW (2021) What is Artificial Immune System? Int J Swarm Evol Comput. S6:002.
Copyright: © 2021 Deng XW. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.