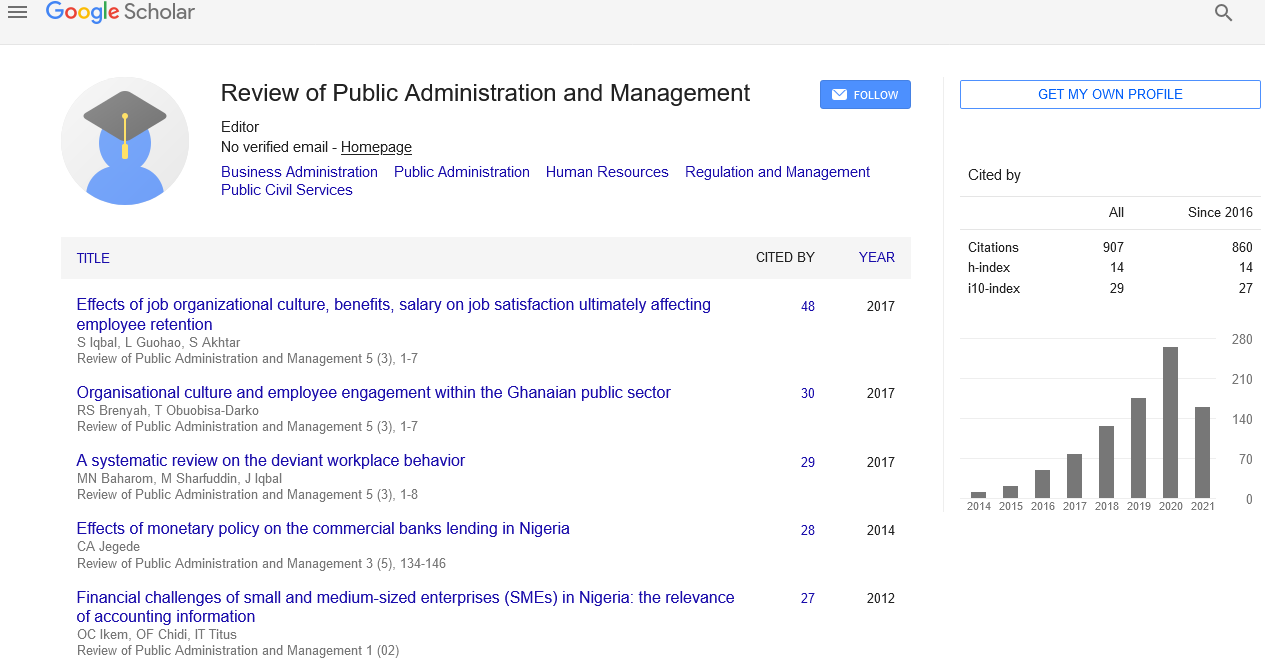
Indexed In
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Scholarsteer
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Commentry - (2022) Volume 10, Issue 1
The Chain-Mediating Role of Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment
Zheng Lai*Received: 07-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. RPAM-22-14860; Editor assigned: 10-Jan-2022, Pre QC No. RPAM-22-14860 (PQ); Reviewed: 21-Jan-2022, QC No. RPAM-22-14860; Revised: 27-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. RPAM-22-14860(R); Published: 03-Feb-2022, DOI: 10.35248/2315-784 4.22.10.1000324
Description
Although it is widely accepted that the causal relationship between work satisfaction and organizational involvement remains highly debated, psychological contract theory makes work satisfaction a powerful predictor of organizational involvement. For example, a highly satisfied employee can develop strong loyalty and mutual commitment immediately after understanding and accepting an organization’s goals and values. Therefore, it seems more reasonable that the organizational commitment of civil servants can be influenced, at least in part, by their job satisfaction. In other words, civil servants who are highly satisfied with their work are more likely to concentrate on their work or organization. According to psychological contract theory, when employees are satisfied with salaries, work autonomy, professional training, and career development, their commitment to the organization increases, which leads to positive performance behavior. As mentioned earlier, many studies have confirmed that employee turnover intentions can be significantly predicted by both job satisfaction and organizational involvement. For example, according to Vandenabeele (2009), civil servant job satisfaction and organizational commitment acted as an intermediary in the relationship between PSM and performance. These results were further supported by those who claimed that PO suitability and organizational involvement mediated the link between PSM and the organization’s civic behavior. In addition, some empirical studies have proposed a structural sales model that combines both work satisfaction and organizational involvement into a single model. Therefore, based on the above discussion and hypothesis, we expect work satisfaction and organizational involvement to act as a chain mediator between PSM and intent to leave. In short, PSM first helps to increase employee job satisfaction, which has a positive impact on employee loyalty and organizational commitment, and then a positive work-related attitude. You can effectively reduce your willingness to quit your job. Therefore, this leads to the following hypothesis. Data from this survey were collected from August- September 2019 from MPA (Master of Public Administration) students at two prestigious universities in Yunnan, China. Prior to the survey, we contacted the directors of the MPA Education Centers at each university to obtain data on the total number of MPA students. With the help of MPA Training Center staff, we distributed a series of questionnaires to 600 MPA students who are full-time civil servants in various government departments. Each participant was asked to fill out a self-assessment questionnaire voluntarily and anonymously. After deleting the 13 questionnaires with missing data, we obtained a diverse sample of 587 participants who are full-time civil servants employed by local governments at all levels throughout Yunnan. Of the participants, 306 (52.1%) were male and 281 (47.9%) were female. 42.2% of the participants were under 30 years old and 13.1% were over 50 years old. In terms of educational background, 74.8% have at least a bachelor’s degree and 25.2% have an associate degree or lower. Regarding the employment period, 31.2% worked for less than 5 years, 23.5% worked for 6-10 years, 8.7% worked for 11-15 years, 7% worked for 16-20 years, and 29.6% worked for 21 years or more.
Motivation for Public Services
Motivation for public services was measured using a translated version of five items developed by Perry (1996) and widely used in various cultural contexts. These 5 points are used to evaluate the four aspects of an individual’s PSM, including self-sacrifice (2 points), public interest efforts (1 point), compassion (1 point), and social justice (1 point). I did. The sample item was, “Making a difference in society is more meaningful to me than personal achievement.” Each item is measured on a 5-point Likert scale from 1 (very disagreeable) to 5 (very disagreeable). Cronbach’s alpha was 0.835.
Rewarding Work
Job satisfaction was assessed on a four-point scale using the Boateng and Hsieh (2019) scale. As an example, there were comments such as “I will not give up my current job no matter what” and “I am totally satisfied with my current job”. Participants answered items on a 5-point Likert scale from 1 (very disagreeable) to 5 (very disagreeable). Cronbach’s alpha was 0.839.
Analytical Strategy
Data analysis was performed using SPSS and AMOS version 24. The missing values were processed with full information maximum likelihood before analysis. As recommended by Anderson and Gerbing (1988), a two-step analytical strategy was used to perform the data analysis. To determine if all study variables were identifiable in the current study, we first tested and compared the model fits of the four models using Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA). The hypothetical model was evaluated against the alternative model by confirmed factory analysis. To avoid the risk of common method bias in self-administered studies, common method bias was tested using Herman’s single factor analysis. Next, to test the hypothesis, study performed structural equation modeling in AMOS 24 to see if the relationship between PSM and severance intentions was mediated by work satisfaction or organizational involvement.
Before investigating the effect of mediation, mainly first tested the direct effect of PSM on employees’ intentions to retire without including mediators in the structural equation model. Next, this study analyzed the indirect and mediation effects using the bias-corrected bootstrap method of the mediation test. If zero is outside the confidence interval, the mediation effect is statistically significant.
Citation: Lai Z (2022) The Chain-Mediating Role of Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment. Review Pub Administration Manag. 10:324.
Copyright: copy&; 2022 Lai Z. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.