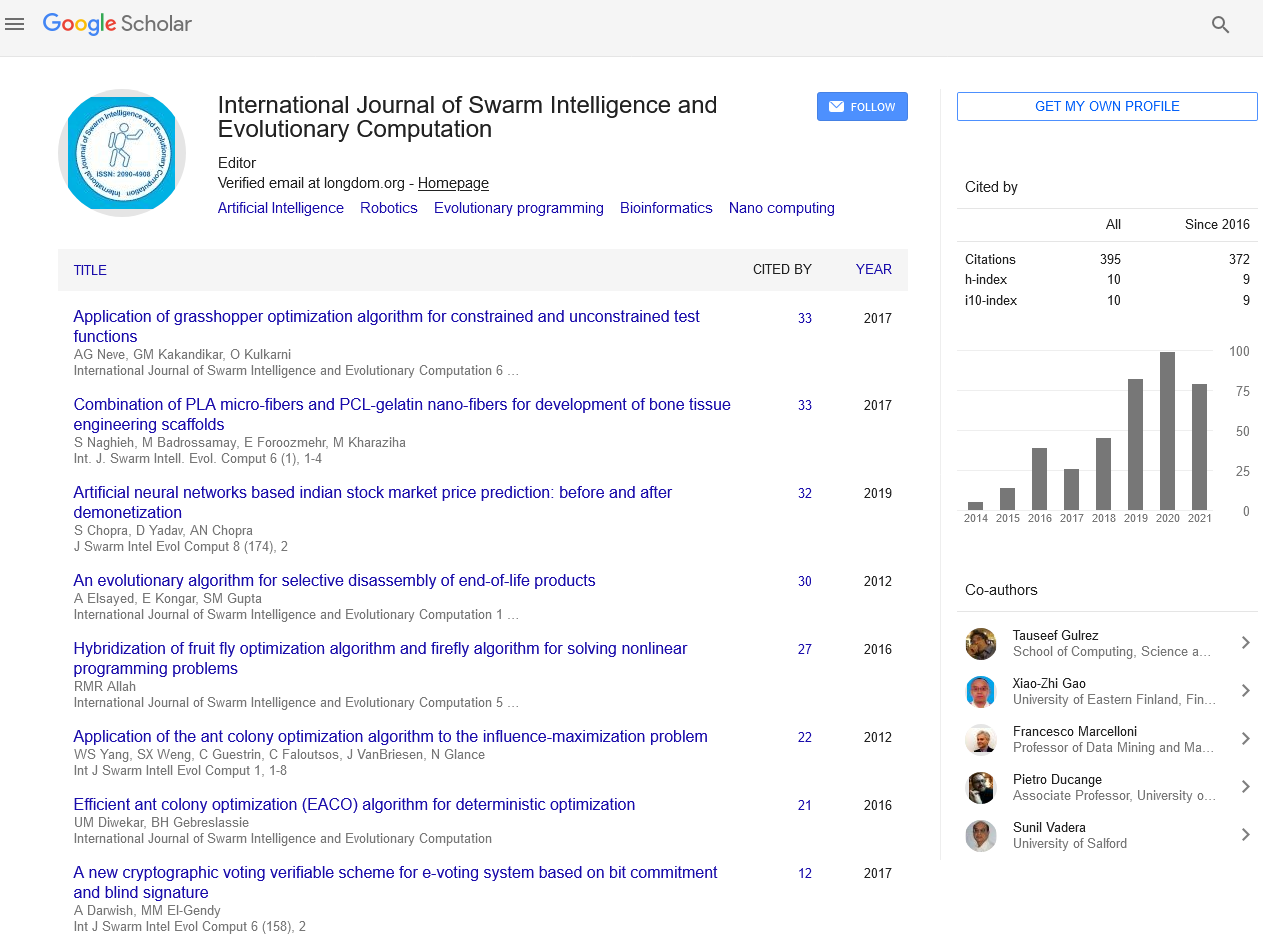
Indexed In
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Perspective - (2022) Volume 11, Issue 11
Significance of Cryptography in Network Security
Yuang Leo*Received: 17-Oct-2022, Manuscript No. SIEC-22-19343; Editor assigned: 19-Oct-2022, Pre QC No. SIEC-22-19343 (PQ); Reviewed: 31-Oct-2022, QC No. SIEC-22-19343; Revised: 07-Nov-2022, Manuscript No. SIEC-22-19343 (R); Published: 17-Nov-2022, DOI: 10.35248/2090-4908.22.11.283
Description
Cryptography, also known as cryptology, is the act or practice for secure communication in the presence of adversarial behavior. More broadly, cryptography is concerned with the development and analysis of protocols that prevent third parties or the general public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the crossroads of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and other disciplines. The fundamental concepts of information security (data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation) are also central to cryptography. Cryptography's practical applications include electronic commerce, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, computer passwords, and military communications.
Prior to the modern era, cryptography was effectively synonymous with encryption, converting readable data to unintelligible nonsense text that can only be read by reversing the process. To prevent adversaries from gaining access to an encrypted (coded) message, the sender only shares the decryption (decoding) technique with the intended recipients. Since the invention of rotor cypher machines in World War I and the introduction of computers in World War II, cryptography methods have become more complex and diverse in their applications.
Cryptosystem Model The use of a neural network provides high security. Together, neural networks and cryptography can be of great assistance in the field of network security. The neural network's key is in the form of weights and neuronal functions, and it is difficult to break. In this case, content data would be used as an input data for cryptography, rendering data unreadable to attackers while remaining secure from them. Mutual learning, self-learning, and stochastic behavior of neural networks and similar algorithms can be used for various aspects of cryptography, such as public-key cryptography, key distribution problem solving using neural network mutual synchronization, hashing, or generation of pseudo-random numbers. Another idea is for a neural network to use "bias" to divide space into non-linear chunks. It provides various probabilities for activating or deactivating the neural network. This is extremely useful in Cryptanalysis.
A network administrator's provisions and policies for preventing and monitoring unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or denial of a computer network and network-accessible resources are referred to as network security. Network security encompasses a wide range of computer networks, both public and private, that are used in day-to-day transactions and communications between businesses, government agencies, and individuals. Private networks, such as those within a company, can exist alongside public networks. It does exactly what the title implies and it secures the network while also protecting and monitoring operations. The most common and straightforward method of protecting a network resource is to give it a unique name and a corresponding password.
Significance
Cryptography and network security are two networking terms for data and network protection and security. Cryptography is used to protect private information shared between two communicating parties from being intercepted by a third party. The primary principles of cryptography are confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation. Client data is protected by network security, which ensures that hackers cannot easily gain access to network.
Network security also improves network performance by preventing the system from being slowed down by redundant tools and data. To safeguard the network against a ransomware attack. Ransomware is a type of attack that prevents from accessing data until pay the ransom. Above all, cryptography protects the sender message by converting it into an unreadable format while it is transmitted over the network, preventing unauthorized users from accessing.
Citation: Leo Y (2022) Significance of Cryptography in Network Security. Int J Swarm Evol Comput. 11:283.
Copyright: © 2022 Leo Y. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.