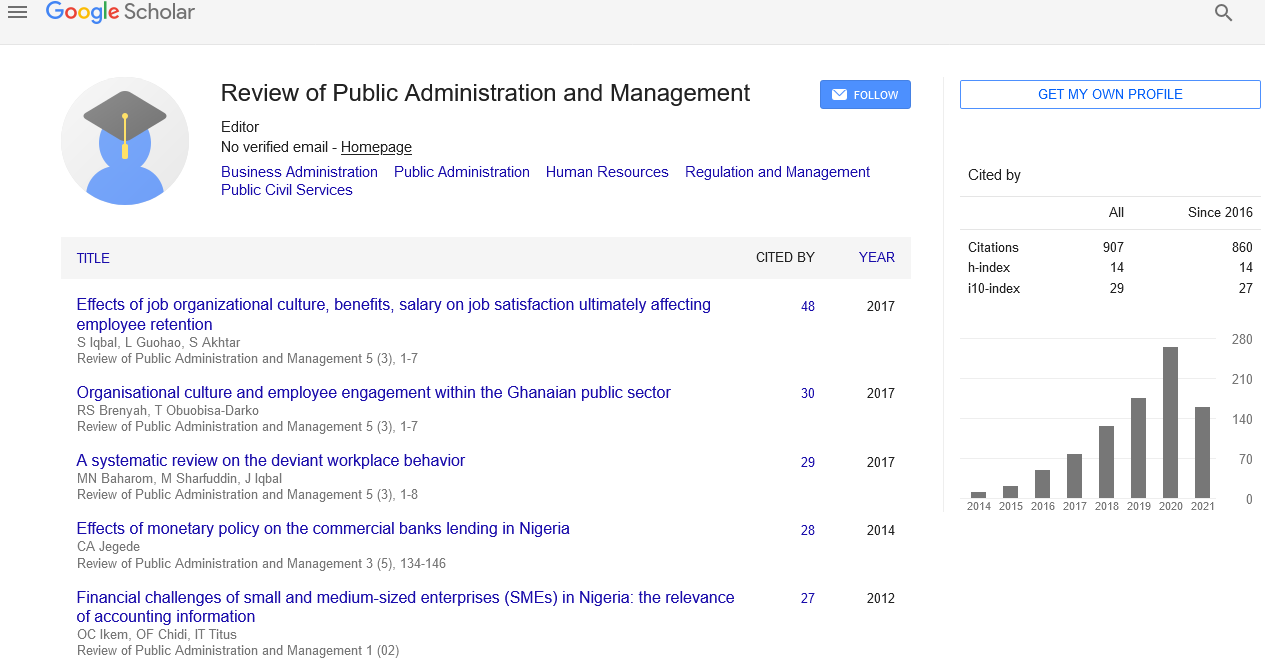
Indexed In
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Scholarsteer
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Perspective - (2022) Volume 10, Issue 3
Rural Development- Increasing Economical Growth
Ziyan Wu*Received: 07-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. RPAM-22-16236; Editor assigned: 10-Mar-2022, Pre QC No. RPAM-22-16236 (PQ); Reviewed: 24-Mar-2022, QC No. RPAM-22-16236; Revised: 31-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. RPAM-22-16236 (R); Published: 07-Apr-2022, DOI: 10.35248/2315-7844.22.10.333
Description
In recent years, attention has been drawn to the question of whether the well-being of the poor in developing countries is negatively affected by status concerns, as has been demonstrated for the poor, richer than them, both in the developed world and in the developing world. A common empirical approach to answering this question is to associate happiness with relative economic position, while controlling for absolute economic position and a set of covariates. Relative economic position is measured by income level or by consumption level. Studies addressing this issue do not send a consistent message. The results vary across countries with similar rankings at the bottom of the global economic scale. In Nepal, he showed that relative consumption affects subjective well-being even at absolute or relatively low levels of consumption.
Rural development is the process of improving the quality of life and the economy of people living in rural areas, which are often relatively isolated and sparsely populated. Rural development has traditionally focused on the exploitation of land-intensive natural resources such as agriculture and forestry. However, changes in global production networks and increasing urbanization have changed the characteristics of rural areas. Increasingly, tourism, manufacturing and niche entertainment have replaced resource extraction and agriculture as the dominant economic drivers. The need for rural communities to approach development from a broader perspective has created a greater focus on multiple development goals than simply creating incentives for agro or agricultural-based businesses resources. Education, entrepreneurship, physical and social infrastructure all plays important roles in the development of rural areas. Rural development is also characterized by its importance to local development economic development strategies. Unlike urban areas, which have many similarities, rural areas have many differences. For this reason, there are many rural development approaches used around the world.
Rural development is generally a method of improving the quality of life and financial well-being of individuals, especially living in densely populated and remote areas. Traditionally, rural development has focused on the misuse of land-intensive natural resources such as forestry and agriculture. But today, increasing urbanization and changing global production networks have changed the nature of rural areas. Rural development remains the focus of the overall development of the country. More than two-thirds of the country's population depends on agriculture for their livelihood, and a third of rural India still lives below the poverty line. Therefore, it is important for governments to operate efficiently and provide sufficient facilities to improve their standard of living.
Importance of rural development
Rural development is important not only for the majority of people living in rural areas, but also for the economic expansion of the country as a whole. Rural development is more important than ever in the country's development process. This is a strategy to achieve and productivity gains, higher socio-economic fairness and ambitions, and stable socio-economic development. Its main task is to mitigate the famine of about 70% of the rural population and provide adequate and healthy food. The secondary task is to ensure the availability of clothing and shoes, a clean environment and home, medical, recreational facilities, education, transportation and communication.
• Improving productivity and wages in the countryside
• Ensure job opportunities increase and quickly To eliminate
• Unemployment and reduce the underemployment rate significantly
• Ensuring the improvement of living standards of the poor population
• Ensure basic needs: primary education, health care, drinking water, rural roads, etc.
The success of the Millennium Development Goals is on the centre of sustainable improvement. Sustainable rural improvement is important to the economic, social and environmental viability of nations. It is important for poverty eradication on the grounds that international poverty is overwhelmingly rural. The manifestation of poverty is going past the urban-rural divide; it has sub regional and local contexts. It is consequently critical, and there may be notable price to be gained, through coordinating rural improvement tasks that make contributions to sustainable livelihoods via efforts on the international, local, country wide and neighborhood levels, as appropriate. Strategies to cope with rural improvement have to think about the remoteness and potentials in rural regions and offer focused differentiated approaches.
A healthy and vibrant agricultural sector is an important foundation for rural development, creating close links with other economic sectors. Rural livelihoods are improved through the effective participation of rural people and rural communities in managing their own social, economic and environmental goals by empowering rural people villages, especially women and young people, through organizations such as local cooperatives and by adopting a bottom-up approach. The close economic integration of rural areas with neighbouring urban areas and the creation of rural off-farm jobs can reduce rural-urban disparities, widen opportunities, and encourage retaining skilled people, including youth, in rural areas. There is considerable potential for rural job creation not only in agriculture, agribusiness and rural industry, but also in rural infrastructure construction, sustainable management of natural resources, and sustainable development. Rural communities in developing countries still face challenges related to access to basic services, economic opportunities, and the degree of inconsistency in planning associated with segregation rural-urban division.
Citation: Wu Z (2022) Rural Development- Increasing Economical Growth. Review Pub Administration Manag. 10:333.
Copyright: © 2022 Wu Z. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.