Indexed In
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
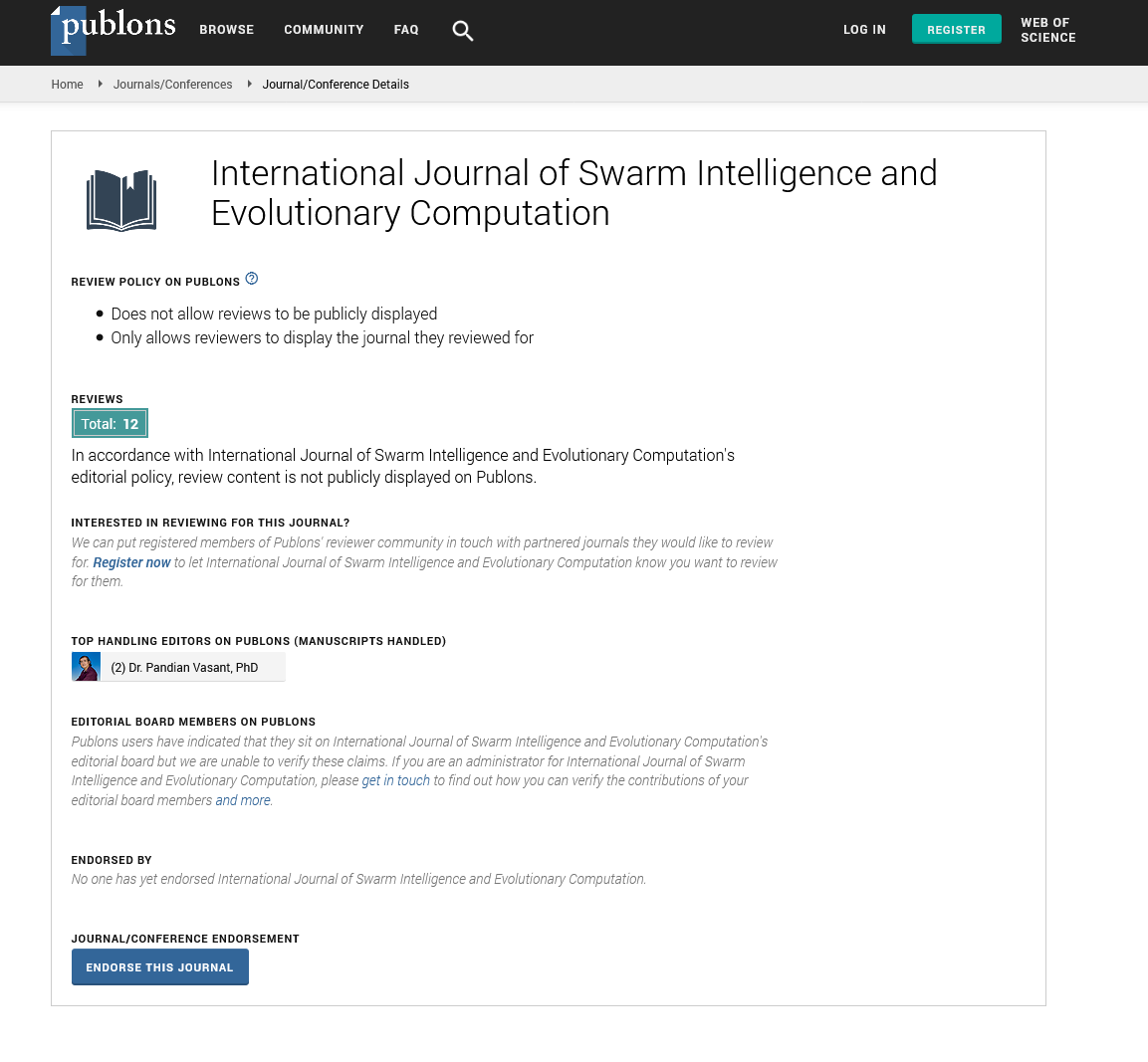
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Commentary - (2021) Volume 10, Issue 7
Knowledge Modeling and its Operations
Mehrdad Rostami*Received: 06-Dec-2021 Published: 31-Dec-2021
Description
Knowledge modeling is a process of creating a computer interpretable model of knowledge or standard specifications about a kind of process and/ or about a kind of installation or product. The performing knowledge model can only be computer interpretable when it’s expressed in some knowledge representation language or data structure that enables the knowledge to be interpreted by software and to be stored in a database or data exchange train.
Knowledge- based engineering or knowledge- backed design is a process of computer- backed operation of similar knowledge models for the design of products, installations or processes. The design of products or installations also uses the knowledge model to guide the creation of the installation or product that need to be designed. In other words, it used knowledge about a kind of object to produce a product model of an (imaginary) individual object. Also, the design of a particular process implies the creation of a process model, which design exertion can be guided by the knowledge that’s contained in a knowledge model about such a kind of process. The performing process model, product model or installation model is generally also stored in a database.
Operations
Eventually Knowledge Models will be used for any complex task including “design” and “planning”. Moment still, the most important use of KCM is operations appertained to as “Intelligent or Smart Applications”. These are operations and Tools that make unequivocal use of knowledge as exercise-and re-fineable factors, covering following areas.
Monitoring and discovery
In these operations, Knowledge Models give capabilities to cover and descry vicious conditioning, abnormalities; patterns or trends and detector conduct as a result. The conduct can cover a variety of scripts ranging from dispatch & SMS announcement to automated case running.
Suppose of network intrusion or credit card fraud discovery systems as the egregious operations in this order. Still, besides operations that have Monitoring and Discovery as their primary operation, this functionality can be added to important other type of operations to give cumulative benefits on top of the main purpose.
Think of a traditional CRM system that can be stoked with a Knowledge Model to cover shaping trends in channel, profit or client service calls; or an Account or HR system that can be enhanced to descry policy violations.
Adaption and Recommendation
Knowledge Models are laboriously employed in profiling and conforming to surroundings, users and customer’s needs, habits and interests. This allows for advanced quality of tone- service and effective personalization in variety of operations ranging from targeted advertising and product recommendation to blog and news websites.
Good examples of this application are companies similar as Netflix and Match.com that at some point decided to emphasize their focus on sophisticated Knowledge Models for recommendation. And, who are ever since perfecting these Knowledge Models by a dedicated team.
Formalization and Robotization
Numerous businesses, functional and system processes are completely or incompletely automated using some kind of software. In this order, Knowledge Models mandate and coordinate prosecution of a series of human and system conditioning as a controlled sequence within a regular, systematized frame.
Citation: Rostami M (2021), Knowledge modeling and its operations. Int J Swarm Evol Comput. 10:228.
Copyright: © 2021 Rostami M. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.