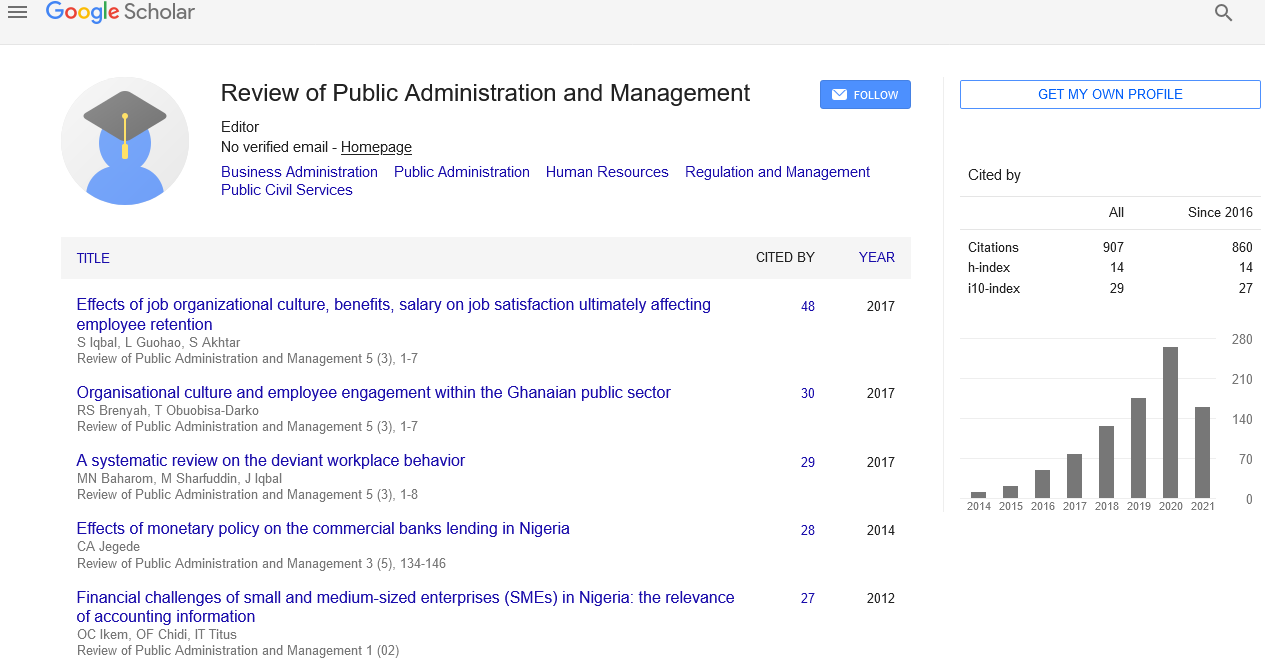
Indexed In
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Scholarsteer
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Opinion Article - (2022) Volume 10, Issue 8
Integrated Social Network Marketing Statistic for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
Naoki Hiro*Received: 05-Aug-2022, Manuscript No. RPAM-22-17942; Editor assigned: 08-Aug-2022, Pre QC No. RPAM-22-17942 (PQ); Reviewed: 22-Aug-2022, QC No. RPAM-22-17942; Revised: 29-Aug-2022, Manuscript No. RPAM-22-17942 (R); Published: 05-Sep-2022, DOI: 10.35248/2315-7844.22.10.360
Description
Social networking has become a cutting-edge marketing technique in the Business-To-Business (B2B) marketing space that holds a lot of potential. At the same time, emerging B2B practices and studies have appeared. B2B businesses are adopting social network marketing more frequently to boost their reputation and obtain a competitive advantage in today's constantly linked world. Although social network marketing can be used in a variety of ways, in the B2B setting, social networks have primarily been seen as platforms that enable businesses to locate new business possibilities or partners, develop new relationships, and reinforce existing ones through constant communication. Despite the numerous potential advantages of adopting social media for B2B, SME marketers in the sector frequently believe social networks to be useless and struggle with implementation. For SMEs, a number of internal and external variables make it difficult to integrate social network marketing analytics into business plans.
The elements influencing Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) adoption of social media marketing were examined using the Technological Organizational Environmental (TOE) paradigm. The strength of the TOE model lies in its flexibility in foretelling the degree of ICT adoption by firms. There is numerous on the positive impacts of TOE factors on the adoption of cutting-edge technologies in the body of extant literature. Unfortunately, the insights cannot be directly applied to the adoption of social media marketing in SMEs because the influence of TOE aspects differs depending on the nature of the organization, the research region, and the technology used. Each innovation is unique, and a variety of factors go into its widespread adoption. The TOE parameters differ depending on the business size, and results from large-firm research cannot be extrapolated and applied to SMEs. The huge differences in resource availability, organizational culture, communication skills, and environmental conditions between SMEs and large organisations have an impact on the applicability of TOE components for adopting a particular technology. In order to understand the factors that influence social media marketing among SMEs, a special strategy is needed. The degree to which TOE conditions affect a company's adoption of innovation is also determined by the variety of environmental conditions and the country-specific regulations. Undoubtedly, this individual situation necessitates taking particular variables into account. Additionally, earlier studies have shown that businesses typically react favourable to circumstances when there is a fear of losing their competitive advantage.
As a result, the highly competitive business environment encourages companies to adopt new technology in order to stay ahead of the competition. As a result, businesses like SMEs in a cutthroat market must spend more on social media marketing to stay competitive and get an edge. Furthermore, the accessibility of financial resources may encourage SMEs to implement social media marketing, especially in a cutthroat sector. In contrast, even when the resources are widely accessible, companies and organisations in non-competitive marketplaces won't use them for social media marketing reasons. This study intends to examine the moderating influence of competitive pressure on the effects of technological, environmental, and organizational factors on the adoption of social media marketing by taking into account the amount to which competition plays a part in the decision-making process of enterprises. The findings of this study add to the body of literature by identifying the variables that influence SMEs' adoption of social media marketing in relation to the level of industry competitiveness.
This helps in many different ways. First, by including a number of elements pertinent to SMEs' adoption of social media, this analyses the multi-perspective framework. Second, by examining the moderating influence of competitive industry to ascertain its impact on the adoption of social media in Malaysia, this study adds to the body of knowledge already in existence. This was done largely to provide a more comprehensive knowledge of the factors that influence and drive social media adoption in Malaysia. Thirdly, several earlier studies on the adoption of social media that used Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) were only able to look at the compensatory and linear relationships between the constructs, which is regarded as being insufficient.
Its capacity to estimate the complexities affecting the complex decision-making processes of SMEs is insufficient. Therefore, as the second stage of study involving a single hidden layer, researchers have used machine learning techniques like Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) to eliminate such limitations. A shallow type of ANN is the second stage ANN analysis with a single hidden layer. Thus, the usage of a deep ANN architecture with two hidden layers was advised. The effectiveness of non-linear connections in the suggested model will be increased by the implementation of a deep ANN architecture with two or more hidden layers due to its deep learning capabilities. The improvements of gap by investigating both non-linear and linear compensating correlations with a dual-stage deep learning approach. It is certainly a cutting-edge technique to use a deep learning dual-stage approach to analyse the drivers of social media adoption by Malaysian SMEs in order to enhance performance. It makes a novel contribution to the body of literature already available on social media adoption, especially in terms of broadening the national perspective.
Citation: Hiro N (2022) Integrated Social Network Marketing Statistic for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses. Review Pub Administration Manag. 10:360.
Copyright: © 2022 Hiro N. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.