Indexed In
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Euro Pub
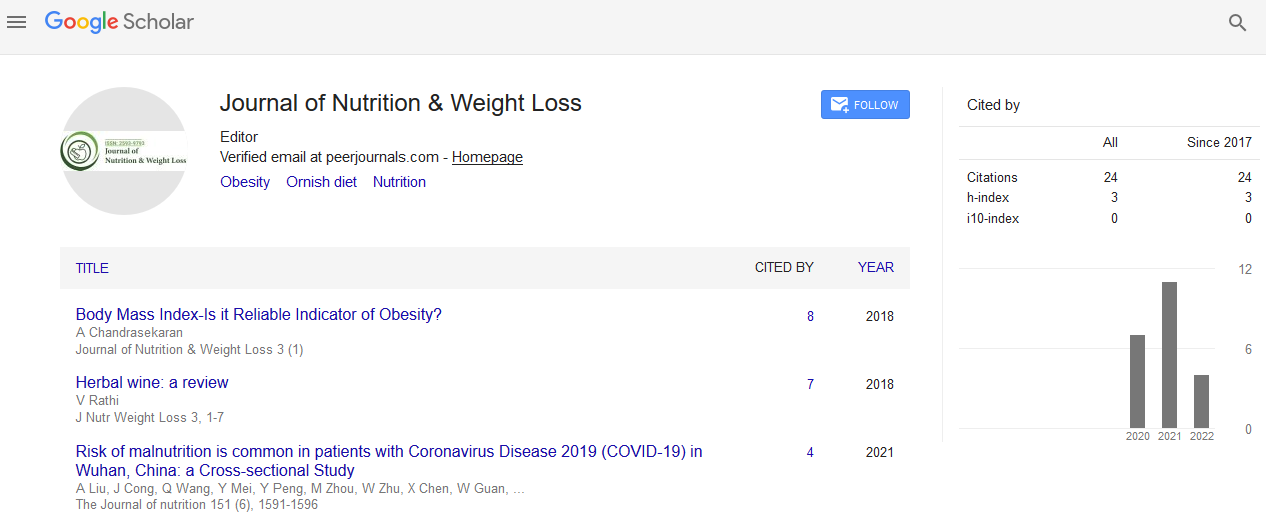
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Commentary - (2025) Volume 10, Issue 4
Nutrient-Focused Diets for Healthy Weight Management
Lucas Whitman*Received: 25-Nov-2025, Manuscript No. JNWL-25-30807; Editor assigned: 28-Nov-2025, Pre QC No. JNWL-25-30807 (PQ); Reviewed: 12-Dec-2025, QC No. JNWL-25-30807; Revised: 19-Dec-2025, Manuscript No. JNWL-25-30807 (R); Published: 26-Dec-2025, DOI: 10.35248/2593-9793.25.10.250
Description
Weight loss diets are widely recognized for their role in supporting individuals who aim to improve health and manage body weight effectively. A successful diet focuses on nutrientdense foods, caloric moderation and consistent eating patterns rather than temporary restrictions or fad methods. Approaching weight loss through structured and balanced dietary changes helps ensure that the body receives essential nutrients while reducing excess energy intake, which supports gradual and sustainable results. One of the central principles of effective weight loss diets is portion control. Consuming smaller portions, while maintaining the nutritional quality of meals, allows individuals to reduce total energy intake without experiencing severe hunger or nutrient deficiencies. This can be achieved by planning meals in advance, using smaller plates and incorporating high-volume, low-calorie foods such as vegetables, fruits and whole grains. Foods rich in fiber not only provide bulk but also prolong satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating between meals.
The role of macronutrients is another critical consideration in diet planning. Proteins help maintain lean muscle mass during weight reduction and promote a feeling of fullness. Lean protein sources, including poultry, fish, eggs, legumes and low-fat dairy, are often emphasized in weight loss plans. Carbohydrates, when derived from whole grains, vegetables and fruits, supply energy for daily activities and support stable blood sugar levels. Healthy fats, including those from olive oil, nuts, seeds and fatty fish, contribute to satiety and aid in the absorption of essential fatsoluble vitamins. A balance of macronutrients ensures that the diet is not only effective for weight reduction but also supportive of overall health.
Hydration is often underestimated in weight management. Adequate water consumption supports metabolic processes, helps reduce the sensation of hunger and may even enhance physical performance. Replacing sugar-laden beverages with water or unsweetened options can decrease unnecessary caloric intake and contribute to weight loss over time. For individuals who enjoy variety, herbal teas or infused water with fruits and herbs provide a flavorful alternative without adding calories. Behavioral strategies are key to achieving long-term success with weight loss diets. Mindful eating, which encourages focusing on the sensory experience of food and recognizing hunger cues, can prevent overconsumption. Tracking meals, identifying triggers for excessive eating and establishing structured meal times contribute to consistency in dietary habits. Planning and preparation, such as cooking meals at home and avoiding highcalorie convenience foods, also enhance adherence to a weight loss diet.
Regular physical activity complements dietary adjustments by increasing energy expenditure and supporting lean body mass. A combination of cardiovascular exercises, such as brisk walking or cycling and resistance training promotes the use of stored fat while maintaining muscle tissue. Exercise also positively affects energy levels, mood and stress management, which are important factors in maintaining adherence to dietary changes. Individual factors such as age, metabolism, activity level and underlying medical conditions influence the effectiveness of a weight loss diet. Consulting a registered dietitian or nutrition professional can provide personalized guidance, helping to establish realistic goals, calculate appropriate caloric intake and select nutrient-rich foods. Such professional support ensures that the diet is both safe and effective for the individual’s unique circumstances.
Sustainable weight loss diets emphasize gradual adjustments rather than extreme measures. Highly restrictive approaches may lead to short-term results but are difficult to maintain and can result in nutritional deficiencies. Small, manageable changes such as increasing vegetable consumption, reducing added sugars and incorporating regular physical activity can collectively lead to meaningful and lasting outcomes. Support from family, friends or peer groups can also enhance adherence to a weight loss diet. Encouragement and shared experiences provide accountability and motivation, especially during challenging periods. Tracking progress, whether through measurements, journals or apps, reinforces the effectiveness of dietary changes and maintains engagement over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, weight loss diets that focus on nutrient quality, portion control, balanced macronutrients, hydration and behavioral adjustments provide an effective approach to managing body weight. When combined with regular physical activity and personalized strategies, these diets can lead to gradual and sustainable improvements in health. Understanding the importance of balanced nutrition and long-term adherence is essential for achieving lasting results while supporting overall wellness.
Citation: Whitman L (2025). Nutrient-Focused Diets for Healthy Weight Management. J Nutr Weight Loss. 10:250.
Copyright: © 2025 Whitman L. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.