Indexed In
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- NSD - Norwegian Centre for Research Data
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Short Communication - (2021) Volume 10, Issue 5
Brief Exchanges on Selection of Genomic Regions and Genes Related to Adaptation and Fertility Traits of Two Colombian Creole Cattle Breeds
C. De Leon1* and R. Martinez22Department of Genetics, Corporación Colombiana de Investigación Agropecuaria-Agrosavia, Mosquera, Cundinamarca, Colombia
Received: 30-Aug-2021 Published: 20-Sep-2021, DOI: 10.35248/2161-1041.21.10.201
Abstract
Natural selection and domestication in livestock species are one of the main evolutive changes resulting in phenotypic adaptations; these patterns create genetic signatures within the genome. To discovery signatures and genes involved in adaptation and fertility traits in two Colombian creole cattle breeds Blanco orejinegro (BON) and Sanmartinero (SM) in the present study it was detected selected genomic regions by comparing differences in regional linkage disequilibrium (LD) using 58,868 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from BON and 57482 SNPs from SM. Also was estimated the variation of genome-wide LD between populations using the VARLD program. The top 0.1 and 0.01th percentiles of standardized VarLD scores were used as a criterion for all comparisons. Ten regions were detected on chromosomes 3, 5, 11, 15, 18, 21, 22, 23, 25 and 29 and genes in it such as CTDSP2, CES1, CFAP161, CLEC14A, HIPK1, RBM4, KDMID, OLFML3, ATP23, LRRTM1, SLC6A2, DEK, SYT6, KDMID involved in adaptation and fertility traits. These findings open the prospect to develop new studies in other cattle breeds and other livestock species which will serve as support in genetic improvement and conservation programs.
Keywords
Creole breeds; SNPs; Adaptability indexes; LD variation
Description
Many studies developed in livestock species based on Genome wide association study (GWAS) and other, have led to the discovery of genomics regions and genes involved in the expression of adaptability and fertility traits widely used in selection and conservation programs [1]. Therefore, new selection methods as provided in this study, became essential for the progress in this field, so, the selection signatures and genes found in the genome appears promising with most statically power than the other methods applied in selection programme [2].
Blanco orejinegro (BON) and Sanmartinero (SM) Colombian creole cattle breeds have been genetically characterized by Martínez et al. with limited impact because lacked assessing in depth the variation and genetic differences of these two breeds [3]. Genetic differences can be measured through determination of selection signatures what are genomic regions fixed in the genome as a result of artificial or natural selection for reasons such as adaptability or productivity.
Linkage disequilibrium (LD) was studied in ROMO an BON Colombian creole cattle breed by Bejarano, reporting increasing LD from 0.3 (r2>0.3) in both breeds, similar finding was reported by Li et al., and Pérez O'Brien et al., who also reported LD breaks down rapidly in absence of selection [4-6]. In other Bos taurus breeds, to milk and meat production, have been reported r2 ≥ 0.3 at distances less than or equal to 30 Kb (Figure 1 and Table 1) [7,8].
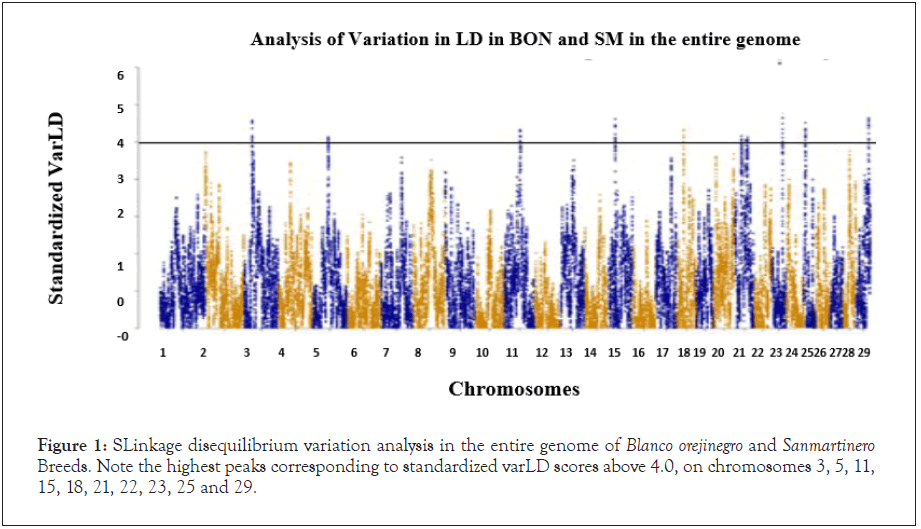
Figure 1: SLinkage disequilibrium variation analysis in the entire genome of Blanco orejinegro and Sanmartinero Breeds. Note the highest peaks corresponding to standardized varLD scores above 4.0, on chromosomes 3, 5, 11, 15, 18, 21, 22, 23, 25 and 29.
| Chr/Percentiles | Regions (bp) | varLD | Standardized varLD scores | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr3 | ||||
| P 0.01 | 29.224.886 | 21.7 | 4.58 | |
| P 0.1 | 29.285.827 | 21.6 | 4.54 | |
| Chr5 | ||||
| P 0.01 | 55.085.241 | 20.3 | 4.13 | ATP23, CTDSP2 |
| P 0.1 | 55.582.528 | 20.2 | 4.10 | |
| Chr11 | ||||
| P 0.01 | 55.683.407 | 20.9 | 4.33 | LRRM1 |
| P 0.1 | 55.443.099 | 20.8 | 4.30 | |
| Chr15 | ||||
| P 0.01 | 24.184.623 | 21.8 | 4.61 | ZW10 24.284.251-24.319.569 |
| P 0.1 | 24.186.798 | 21.3 | 4.45 | |
| Chr18 | ||||
| P 0.01 | 23.903.882 | 20.9 | 4.32 | SLC6A2, CES1 |
| P 0.1 | 23.955.588 | 20.8 | 4.30 | |
| Chr21 | ||||
| P 0.01 | 26.990.623 | 20.3 | 4.15 | CFAP161 |
| P 0.1 | 26.929.649 | 19.9 | 4.02 | |
| P 0.01 | 48.369.157 | 20.2 | 4.12 | SSTR1 |
| P 0.1 | 48.313.773 | 19.9 | 4.01 | |
| Chr23 | ||||
| P 0.01 | 39.339.694 | 23.9 | 5.24 | DEK: 39.355.962-39.387.656 |
| P 0.1 | 39.354.709 | 23.9 | 5.22 | KDMIB: 39.389.854-39.432.004 |
| Chr29 | ||||
| P 0.01 | 44.796.094 | 21.9 | 4.64 | SPTBN2,RBM4B |
| P 0.1 | 44.707.685 | 21.8 | 4.59 |
Table 1: Genomic regions in base pairs (bp) on chromosomes 3, 5, 11, 15, 18, 21, 23, 29. Linkage disequilibrium variations and standardized varLD scores, on percentiles 0.001 and 0.1 and genes found in these regions.
Genes identified in these selected regions consistent with other research work, are involved in the various biological processes from production, reproduction and adaptation and can be used in selection and conservation programs of these Colombian Creole breeds. This study helps to explain the genetic architecture conformed for productive, reproductive and adaptation processes. Different genes identified in these selected regions consistent with other research work, are involved in the various biological processes from production, reproduction and adaptation and can be used in selection and conservation programs of these Colombian Creole breeds.
REFERENCES
- De León C, Manrique C, Martínez R, Rocha JF. Genomic association study for adaptability traits in four Colombian cattle breeds. Genet Mol Res. 2019;18.
- Teo YY, Fry AE, Bhattacharya K, Small KS, Kwiatkowski DP, Clark TG. Genome-wide comparisons of variation in linkage disequilibrium. Genome Res. 2009;19(10):1849-1860.
- Martínez SRA, Gallego GJL, Gómez VY, Moreno LF. Eficiencia productiva de la raza BON en el trópico colombiano. Editorial Salmon D.C. 2012.
- Bejarano GDH, Genomic association study for growth traits in Creole cattle breeds Blanco Orejinegro and Romosinuano. Master of Science Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogotá. 2016.
- Li X, Yang S, Dong K, Tang Z, Li K, Fan B, et al. Identification of positive selection signatures in pigs by comparing linkage disequilibrium variances. Anim Genet. 2017;48(5):600-5.
- O’brien AM, Utsunomiya YT, Mészáros G, Bickhart DM, Liu GE, Van Tassell CP, et al. Assessing signatures of selection through variation in linkage disequilibrium between taurine and indicine cattle. Genet Sel Evol. 2014;46(1):1-4.
- Bolormaa S, Hayes BJ, Savin K, Hawken R, Barendse W, Arthur PF, et al. Genome-wide association studies for feedlot and growth traits in cattle. J Animal Sci. 2011;89(6):1684-1697.
- Larmer SG, Sargolzaei M, Schenkel FS. Extent of linkage disequilibrium, consistency of gametic phase, and imputation accuracy within and across Canadian dairy breeds. J Dairy Sci. 2014;97(5):3128-3141.
Citation: Leon CD, Martinez R (2021) Brief Exchanges on Selection of Genomic Regions and Genes Related to Adaptation and Fertility Traits of Two Colombian Creole Cattle Breeds. Hereditary Genet. 10:201.
Copyright: © 2021 Leon CD, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.