Awards Nomination
20+ Million Readerbase

Indexed In
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
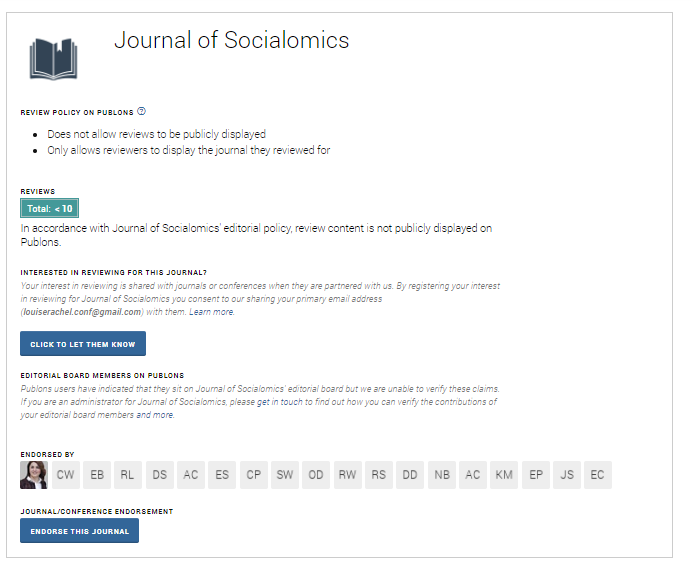
- Publons
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences