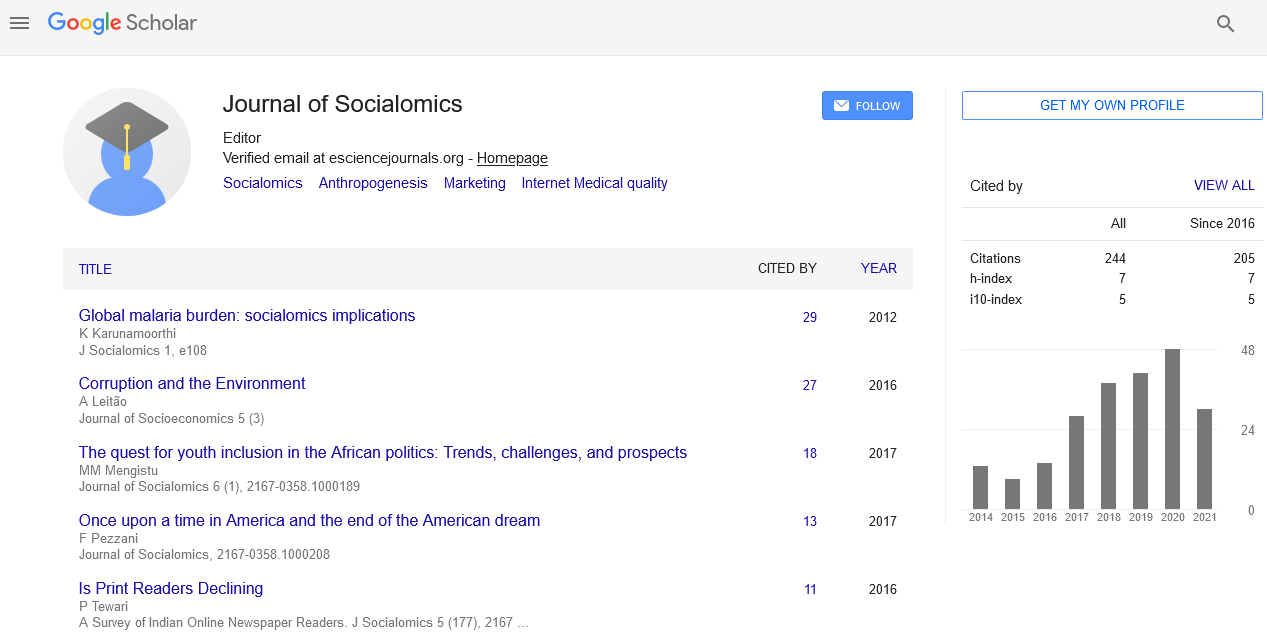
Indexed In
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Opinion Article - (2022) Volume 11, Issue 11
Industrial Economy: Distributed Optimization of Social Welfare and Regulations
Jiaxin Duan*Received: 04-Nov-2022, Manuscript No. JSC-22-18994; Editor assigned: 07-Nov-2022, Pre QC No. JSC-22-18994 (PQ); Reviewed: 21-Nov-2022, QC No. JSC-22-18994; Revised: 28-Nov-2022, Manuscript No. JSC-22-18994 (R); Published: 05-Dec-2022, DOI: 10.35248/2167-0358.22.11.155
Description
Growth and variations in the macroeconomy are significantly influenced by the rate of urbanisation. By limiting the growth in urban population and the rate of urban land construction and development, the government, which serves as the primary regulator of macroeconomic activity, may modify the pace and rhythm of urbanisation while also regulating the macroeconomy and enhancing social welfare. Neither too quick nor too slow may be said to be the rate of urbanisation. If domestic demand grows too slowly, it won't be enough to support sustained economic growth. Long-term economic growth will be constrained by the strict restrictions of resources and the environment, despite the fact that excessive speed might encourage rapid economic growth in the near term. In general, the rate of population growth and land urbanisation has followed the economic cycle. The urbanisation rate is generally quick during periods of relatively rapid economic growth and relatively sluggish during periods of relatively slow economic growth. Urbanization's countercyclical response to macroeconomic swings has not been fully different industries have intricate competitive and collaboration ties that are centered in one particular sector. Each industrial cluster is more sophisticated and at the same time quite distinct. Businesses, suppliers, and financial organisations are united to form the same cluster. Manufacturers, sales channels, and customers are just a few of the several components that make up an industrial cluster.
Clusters of industries are distinct from regular industrial groupings and span a wider range of industries. To play to their own competitive advantages, they can combine multiple institutions and organisations, merge numerous industries in a particular region, and create a symbiosis. To achieve industrial transformation and upgrading, the growth of industrial clusters involves deep integration and processing as well as ongoing production chain expansion. When considering industrial clusters from a micro viewpoint, it becomes clear that businesses grow vertically and internal transactions take the place of external ones. The cost of internal transactions is relatively cheap, which allows businesses to save on development costs. Through integrated development, businesses may sustainably execute the linkages between enterprises. The work and social welfare security system is a key link in the process of developing long-term and stable creative social governance, and there can be an interdependent and coordinated interaction between innovative social governance and that system. For the purpose of building a more comprehensive social welfare security system, it is required to progressively improve the scientific, stability, and sustainability of the social welfare security system and jointly protect the appropriate legal mechanisms. Social welfare security is a fundamental right that all citizens are entitled to, and the labour social welfare security system is a fundamental labour welfare security system that the state has established and implemented one of the most crucial factors in ensuring proper growth is the fact that it is a right that all citizens may enjoy.
The requirements of residents' overall quality of life are not met by labour and social welfare security, which merely offers a type of security that temporarily satisfies the most fundamental living necessities of citizens. Social welfare security is an essential requirement for people's daily existence. Numerous issues have been resolved as a result of the extensive work that has been done in recent years to establish labour social welfare security. The creation of a social insurance system ought to be based on social insurance, assistance, and social welfare, with basic endowment insurance, basic medical insurance, and the improvement of the minimum living security system as the key, complemented by various commercial insurances as supplementary elements and build a more comprehensive labour and social welfare security system as the key pillars sustainable development of a social economy is directly reflected in the effective improvement of the nation's overall strength, and it is also an inevitable prerequisite for realizing the cultural rights and interests of the Chinese people. Social welfare security is a necessary condition for promoting the positive development of culture. To do this, we should investigate the rich cultural history, fully utilize our special assets, and give our special advantages their due consideration, and work to attain specific goals in the creation of a socialist spiritual culture. In order to improve the public cultural system and further optimise and innovate the social welfare security system, it is necessary to allow more local industrial economies to radiate stronger vitality. The vigorous development of the industrial economy will inevitably result in the improvement of the public cultural system.
Citation: Duan J (2022) Industrial Economy: Distributed Optimization of Social Welfare and Regulations. J Socialomics. 11:155.
Copyright: © 2022 Duan J. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.