Indexed In
- Open J Gate
- JournalTOCs
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Scholarsteer
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
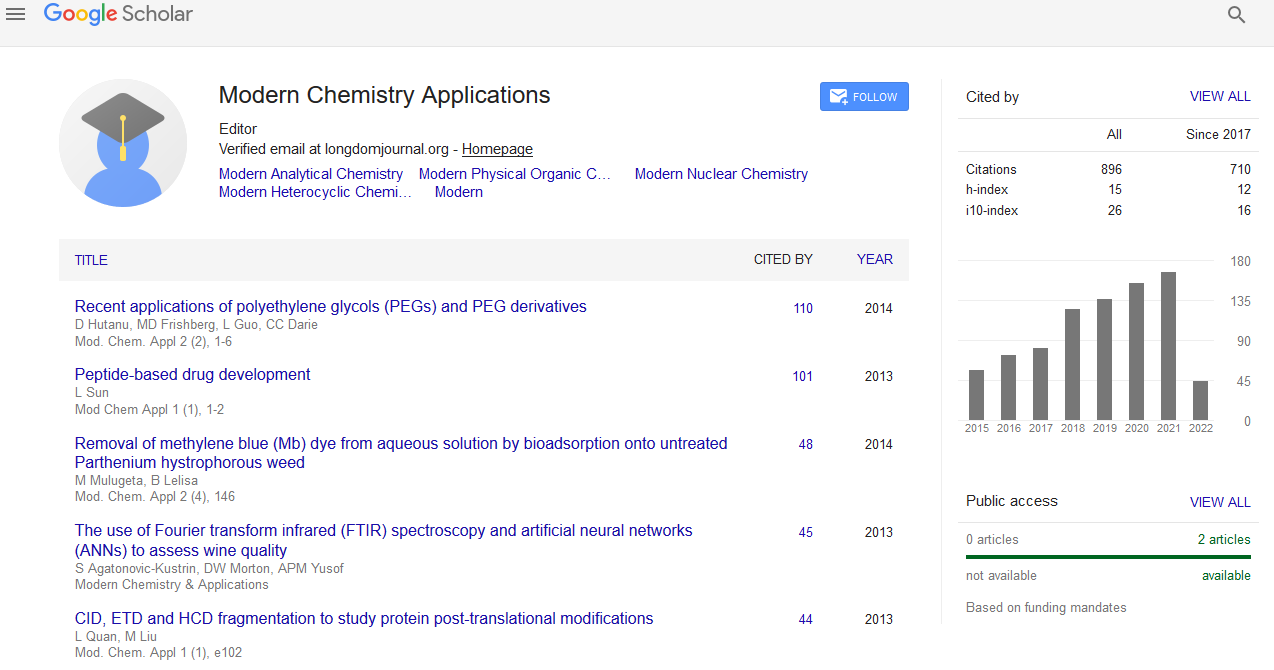
Commentary - (2022) Volume 10, Issue 10
Aspects of Nuclear Reactions and their Emitted Radiation Patterns
Sophia Liam*Received: 29-Sep-2022, Manuscript No. MCA-22-18604; Editor assigned: 03-Oct-2022, Pre QC No. MCA-22-18604 (PQ); Reviewed: 17-Oct-2022, QC No. MCA-22-18604; Revised: 24-Oct-2022, Manuscript No. MCA-22-18604 (R); Published: 31-Oct-2022, DOI: 10.35248/2329-6798.22.10.381
Description
Nuclear chemistry is one of the branch of chemistry which deals with transformations, nuclear processes and radioactivity in the nuclei of atoms, such as nuclear transmutation.
Nuclear reactions and their radiations
There are 3 kinds of radioactive radiations which were identified by Rutherford in 1902 by passing radiations them between two oppositely charged plates.
Radiations which bend towards the negative ion plate carry a positive charge and are called as alpha rays. The radiations which bend towards the positive plate carry a negative charge and are known as beta rays.
The last kind of radiation which is uncharged and passed straight throughout the electric field is called as gamma rays.
Different kinds of radiations:
Nuclear reactions takes place when the transformation of energy from one element into another. This kind of nuclear reactions is used in nuclear power plants to collect nuclear energy. The 3 common kinds of radiations are as follows below.
Alpha radiation: Emission part of alpha particle from an atom’s nucleus emits radiation. The Alpha particle consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons and it is much similar to Helium (He) nucleus. When an atom emits an Alpha particle, the atomic mass of atom decreases by 4 units.
Beta radiation: The mass of atom was not change when Beta particle emitted by an atom and also atomic number increase by one unit.
Gamma radiation: Gamma radiation involves emission of electromagnetic energy from an atom. During this radiation, no particles were emitted. And it does not cause any transmutation of the atoms.
Stimulated nuclear reactions: Most of elements in nature can undergo radioactive decay naturally and for this kind of elements nuclear reactions can be stimulated artificially. Such types of reactions are Nuclear fission and Nuclear fusion.
Nuclear fission
Splitting of atomic nuclei into 2 or lighter nuclei is called as nuclear fission. This kind of process can done by an nuclear reaction or by radioactive decay. Nuclear fission reactions release a large amount of energy and this energy is accompanied by the emission of neutrons and gamma rays.
Nuclear fission was first discovered by an German chemists Hahn and Strassmann in the year of 1938. The energy generated from fission reactions is converted directly into electricity in nuclear power plants. This process is done by using the heat produced from the nuclear reaction and convert water into steam. The collected steam is used to rotate turbines to generate electricity.
Nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion reactions takes place when at least two atomic nuclei fuse into an single nucleus. Subatomic particles such as protons or neutrons are formed as products in these nuclear reactions.
Example of the nuclear fusion reaction which occurs between deuterium (2H) and tritium (3H) that yields helium (4He) and a single neutron (1n). Such fusion reactions occur at the inner core of the sun and other stars. The kind of fusion in deuterium and tritium nuclei is accompanied by a loss of approximately 0.0188 amu of mass (which is completely converted into form of energy). Approximately 1.69*109 kilojoules of energy are generated from every mole of helium formed.
Other Important types of Nuclear Reactions such as follows:
Alpha decay: Nuclei having mass numbers greater than 200 which tend to undergo alpha decay. Alpha decay is an process in which a 4He nucleus, commonly referred to as an alpha particle (42α) is liberated from an parent nucleus.
Beta decay: Beta decay is an process which occurs when a neutron is converted into a proton, which is accompanied by emission of an beta particle. Example for this type of nuclear reaction is the beta decay of carbon-14 which affords nitrogen-14.
Gamma emission: Gamma emission is the process which occurs when an excited nucleus (often produced from the radioactive decay of another nucleus) returns into its ground state, by the emission of a high energy photon.
Conclusion
Nuclear chemistry involves in the study of chemical effects resulting from absorption of radiation within the living plants, animals and other materials. Radiation chemistry controls living things at the molecular scale. It also involves in the study and use of nuclear processes in non-radioactive areas of human activity. For this study Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is commonly technique used in synthetic organic chemistry, physical chemistry, structural analysis and also in macro-molecular chemistry.
Citation: Liam S (2022) Aspects of Nuclear Reactions and their Emitted Radiation Patterns. Modern Chem Appl. 10:381.
Copyright: © 2022 Liam S. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.